Evaluations of Programs with Work-Based Learning








 Internships
Internships
n=2,544RCT
n=2,678RCT
Year Up prepares disadvantaged young adults aged 18 to 24 for a career in the information technology or financial operations fields. Treatment includes 6 months of technical skills training that is validated and regularly updated by industry partners, classes in business communications, and mentorship. Participants are then placed in a 6-month internship with an industry partner guided by a performance contract. Stipends support participants through training and the internship, and job search assistance is available once the internship ends. Year Up leverages a unique funding scheme, including support from industry partners, to spend about $25,000 on each participant.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
$1,895 higher average earnings over sixth and seventh quarters after random assignment* |
Shorter Term: 4-5PP increase immediately after program exit* Longer Term: No significant difference past 1 year after exit* |
Participants were 18PP more likely to earn an industry-recognized credential (and had 1.5 more months of college enrollment per year)* |
Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Fein, D. and Hamadyk, J. (2018). Bridging the Opportunity Divide for Low-Income Youth: Implementation and Early Impacts of the Year Up Program, OPRE Report #2018-65, Washington, DC: Office of Planning, Research, and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The Young Adult Internship Program offers subsidized internships to New York City youth aged 16 to 24 who are disconnected from school and work. Participants spend 2–4 weeks in a job readiness training class before placement in an internship for 10–12 weeks. They are paid minimum wage for 25 hours per week during this time. For 9 months after the internship ends, case managers support participants as they pursue employment, education, training, or enlistment in the military.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
$400 over the 6 months after internships end† |
Shorter Term: 3PP increase in 1st quarter after internships end† Longer Term: No effect past 2nd quarter after internships end |
5.1PP increase in permanent employment rate after 1 year†; 4PP increase in self-esteem† |
Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Skemer, Melanie, Arielle Sherman, Sonya Williams, and Danielle Cummings (2017). Reengaging New York City's Disconnected Youth Through Work: Implementation and Early Impacts of the Young Adult Internship Program. OPRE Report 2017-22. Washington, DC: Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Per Scholas prepares low-income youth and adults for the CompTIA A+ exam for computer service technicians. Training lasts 15 weeks, totaling 500 hours, and includes “life skills” elements in addition to technical modules. Support services include career counseling, job placement with employer partners, post-employment retention services, and interview attire. Some graduates of the program are offered internships with Per Scholas's computer refurbishing center, and some are placed in internships with employer partners.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
$4,663 over the year after program exit* |
Shorter Term: 9PP increase in the year after program end* Longer Term: Longer term outcomes unavailable |
Participants were 12PP more likely to have health insurance‡ |
Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Maguire, Sheila, Joshua Freely, Carol Clymer, Maureen Conway, and Deena Schwartz (2010). Tuning into Local Labor Markets: Findings from the Sectoral Impact Study. Public Private Ventures (P/PV).
 Transitional Jobs
Transitional Jobs
n=1,217RCT
A comprehensive employment program for former prisoners based in New York City, the Center for Employment Opportunities (CEO) provided a paid transitional job opportunity and a suite of supportive services aimed at improving participants' labor market prospects and reducing recidivism. Participants were placed in a 5-day preemployment class, after which they worked in maintenance and repair crews for city and state agencies. They worked 4 days per week and were paid minimum wage at the end of every day. The fifth day was spent meeting with staff and participating in supplementary supportive services. Participants were constantly evaluated by their supervisors, and once they demonstrated good performance on the job, they began work with a job search assistant to find permanent employment.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
No effect |
Shorter Term: No effect in the 1st year after program end† Longer Term: No effect in the 2nd year after program end |
Reduced recidivism by 6.9PP over 3 years after random assignment† |
Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Redcross, Cindy, Megan Millenky, Timothy Rudd, and Valerie Levshin (2012). More Than a Job: Final Results from the Evaluation of the Center for Employment Opportunities (CEO) Transitional Jobs Program. OPRE Report 2011-18. Washington, DC: Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The Transitional Work Corporation (TWC) gave long-term Temporary Assistance for Needy Families recipients transitional jobs and other employment services in an effort to improve participants' labor market prospects and reduce welfare caseloads. TWC's program began with a 2-week orientation on job-readiness skills, after which participants were placed in a transitional job, usually with a government or nonprofit agency, earning minimum wage for up to 6 months. Each week, participants were required to work 25 hours and put 10 hours into activities such as job search, job readiness instruction, or GED exam preparation. Once participants found a permanent job, TWC provided them with job retention services and bonus payments at 6 and 9 months.
Not available
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
No effect |
Shorter Term: No effect in the 1st year after program end Longer Term: No effect in the 3rd year after program end |
TANF & SNAP receipts decreased early on, but effects faded after 6 quarters |
Jacobs, Erin, and Dan Bloom (2011). Alternative Employment Strategies for Hard-to-Employ TANF Recipients: Final Results from a Test of Transitional Jobs and Preemployment Services in Philadelphia. OPRE Report 2011-19, Washington, DC: Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The Personal Roads to Individual Development and Employment (PRIDE) program focused on welfare recipients who claimed exemption from work requirements due to a medical problem, but who were determined through medical evaluation to be “employable with limitations.” From there, participants were placed into one of two tracks: vocational rehabilitation for those with the most significant medical barriers, or work-based education for those with literacy, education, or language barriers. People in both tracks performed unpaid work 3 days per week, with the vocational track performing individualized activities 2 days per week, and the work-based education track performing a classroom-based education activity. Both tracks received job search assistance once they were deemed job ready. Staff followed up with participants for 6 months after they were placed in a permanent job.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
No effect |
Shorter Term: 4.3PP increase in the 1st year after random assignment* Longer Term: 5.1PP increase in the 2nd year after random assignment* |
$818 decrease in cash assistance over 2 years after random assignment* |
Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Bloom, Dan, Cynthia Miller, and Gilda Azurdia (2007). The Employment Retention and Advancement Project: Results from the Personal Roads to Individual Development and Employment (PRIDE) Program in New York City. MDRC. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families.
The Transitional Jobs Reentry Demonstration (TJRD) provided newly released prisoners with temporary minimum-wage jobs offering 30–40 hours of paid work per week. While programs in the demonstration differed slightly across the four implementation sites, generally the jobs were not focused on building occupational skills. Rather, they were aimed at addressing behavior and performance issues that may have emerged. Ancillary services and supports included job search assistance. Two of the sites offered retention bonuses for holding a permanent job for 6 to 9 months.
The evaluation created two treatment groups, which allowed it to isolate the effects of the transitional job placements from the effects of permanent job placement services only.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
No effect |
Shorter Term: No effect in 1st year after program end Longer Term: Longer term outcomes unavailable |
Employment retention bonuses boosted earnings by $1,999 over 2 years‡ |
Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Jacobs, Erin (2012). Returning from Work After Prison: Final Results from the Transitional Jobs Reentry Demonstration. MDRC.
 On-the-Job Training
On-the-Job Training
n=344QED
n=5,069RCT
This quasi-experimental evaluation looks at the employment and earnings results of Workforce Investment Act of 1998 (WIA) on-the-job training (OJT) in South Dakota. Workers in an OJT program are placed with a firm for a trial period stipulated in an employment contract between the firm and the state, in which the state subsidizes a percentage of the worker's wages. Typical contracts last 480 hours, while the maximum is 1,040. After the hours are completed, the firm has an option to retain the worker without the wage subsidy.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
$567 in the 3rd quarter after program exit† |
Shorter Term: 8.6PP increase 1st quarter after program exit* Longer Term: 7.4PP increase 3rd quarter after program exit† |
Women saw 2.3x more earnings gains† and 1.5x more employment rate gains than men (after 3 quarters)† |
Note: Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
McEntaffer, M. J. (2015). The Promise of Worker Training: New Insights into the Effects of Government Funded Training Programs (Doctoral dissertation, The University of Nebraska-Lincoln).
This randomized controlled trial seeks to determine the effects of the availability of core, intensive, and training services offered by the WIA adult and dislocated worker funding streams. Core services include only access to resource rooms, a subset of workshops, and online assessments. Intensive services add case management, job search assistance, career and service receipt planning, and in-person assessments and aptitude tests. Training includes OJT and occupational skills training, as well as adult basic education, literacy, and language training.
Treatment groups were structured into tiers, which allows the evaluation to determine the effectiveness of full services versus only core and intensive, full services versus only core, and core and intensive services versus only core.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
No measurable difference between recipients of basic services such as resource centers, and workshops versus full services, including work-based learning |
Shorter Term: 7.8PP increase in the 5th quarter after random assignment† Longer Term: Longer term outcomes unavailable |
No effect on household receipt of public assistance |
Note: Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
McConnel et al. (2016). Providing Public Workforce Services to Job Seekers: 15-month Impact Findings on the WIA Adult and Dislocated Worker Programs. Mathematica Policy Research and Social Policy Research Associates. U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration, Office of Policy Development and Research.
 Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships
n=3,301 (short term) n=4,082 (long term)QED
n=21,426QED
Registered Apprenticeship (RA) is an occupational-based career training program combining a curriculum of technical instruction with structured on-the-job training. Each RA is tailored to the needs of an employer, who hires the apprentice and commits to training him or her over the long term. Apprenticeships become registered with the U.S. Department of Labor or the appropriate state apprenticeship agency once employers submit standards, or detailed descriptions of the curriculum, on-the-job training plans, and the hours of each that are required for completion. Wage progressions are often a feature of RAs, but they are not a requirement. When participants complete their hours of instruction and on-the-job training, they are granted an industry-recognized credential that nationally certifies them in a specific occupation, such as an electrician or a plumber and pipe fitter.
This study evaluated RA in the state of Washington, looking at earnings, employment rates, and other related outcomes. It also performs a cost-benefit analysis of the dollars Washington puts into RA.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
$3,243 per quarter in 1st–3rd quarters after exit*; $3,511 per quarter in 9th–12th quarters after exit* (in 2005 dollars) |
Shorter Term: 7.8PP increase over 1st–3rd quarters after program exit* Longer Term: 9.8PP increase over 9th–12th quarters after program exit* |
Hours worked per quarter increased by 37 in 1st–3rd quarters after exit; 51 in 9th–12th quarters† |
Note: Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Hollenbeck, Kevin and Wei-Jang Huang (2014). Net Impact and Benefit-Cost Estimates of the Workforce Development System in Washington State. W.E. Upjohn Institute for Employment Research.
Registered Apprenticeship (RA) is an occupational-based career training program combining a curriculum of technical instruction with structured on-the-job training. Each RA is tailored to the needs of an employer, who hires the apprentice and commits to training him or her over the long term. Apprenticeships become registered with the U.S. Department of Labor or the appropriate state apprenticeship agency once employers submit standards, or detailed descriptions of the curriculum, on-the-job training plans, and the hours of each that are required for completion. Wage progressions are often a feature of RAs, but they are not a requirement. When participants complete their hours of instruction and on-the-job training, they are granted an industry-recognized credential that nationally certifies them in a specific occupation, such as an electrician or a plumber and pipe fitter.
This study evaluated the U.S. Department of Labor's RA program across 10 states, looking at earnings, employment rates, and other related outcomes. It also performs a cost-benefit analysis of the federal RA program in those 10 states.
| Earnings Gains | Employment Rates | Other Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
$6,595 in 6th year after RA enrollment*; $5,839 in 9th*; estimated $98,718 over a career* |
Shorter Term: 2.5PP increase in 6th year after RA enrollment* Longer Term: 1.9PP decrease in 9th year after RA enrollment* |
Net social benefits of RA are $58,888 in 9th year; $124,057 estimated over a career |
Note: Statistical significances levels are measured as follows: * = .01, † = .05, ‡ = .10
Reed et al. (2012). An Effectiveness Assessment and Cost-Benefit Analysis of Registered Apprenticeship in 10 States. Mathematica Policy Research. U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration.
![]() Disconnected Youth
Disconnected Youth
![]() Disconnected Adults
Disconnected Adults
![]() Welfare Recipients
Welfare Recipients
![]() Ex-Offenders
Ex-Offenders
Internships Paid, subsidized, or unpaid short term work experience
Transitional Jobs Temporary, subsidized jobs that usually focus on adults with multiple barriers to employment (ex-offenders, TANF recipients, etc)
On-the-Job Training Subsidized jobs for new hires to compensate for on-the-job training costs
Apprenticeship On-the-job training combined with formal job-related instruction, often connected to national skills certificates
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
|---|---|
| QED | Quasi-Experimental Design |
| RA | Registered Apprenticeship |
|---|---|
| PP | Percentage Points |
| TANF | Temporary Assistance for Needy Families |
| SNAP | Supplemental Nutritional Assistance Program |
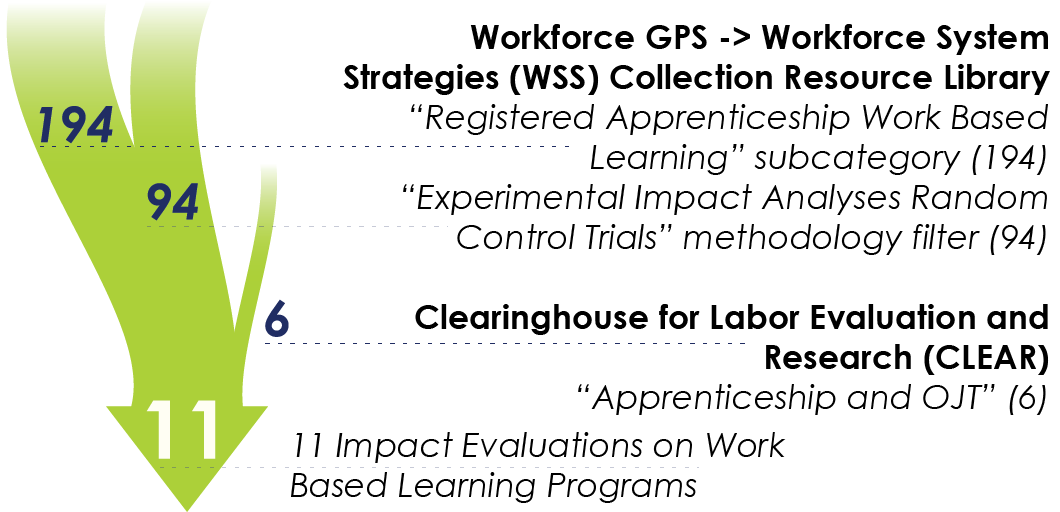

Image Explanation:
A large pool of government-collected evaluations were drawn from when choosing the 11 studies featured on this infographic. In the Workforce System Strategies community on the Department of Labor's WorkforceGPS site, the 194 resources under the “Registered Apprenticeship / Work-based Learning” subcategory were considered as well as the 94 resources under the “Experimental Impact Analyses / Random Control Trials” ” subcategory. In the Clearinghouse for Labor Evaluation and Research, or CLEAR, the 6 resources under the “Apprenticeship and OJT” subcategory were considered.
Click the image above to see a larger version
This info-sheet highlights results from rigorous research studies on programs that include work based learning strategies. These studies were identified through a search of the U.S. Department of Labor's WorkforceGPS and Clearinghouse for Labor Evaluations and Research (CLEAR). See search terms under “Where we Looked.”